

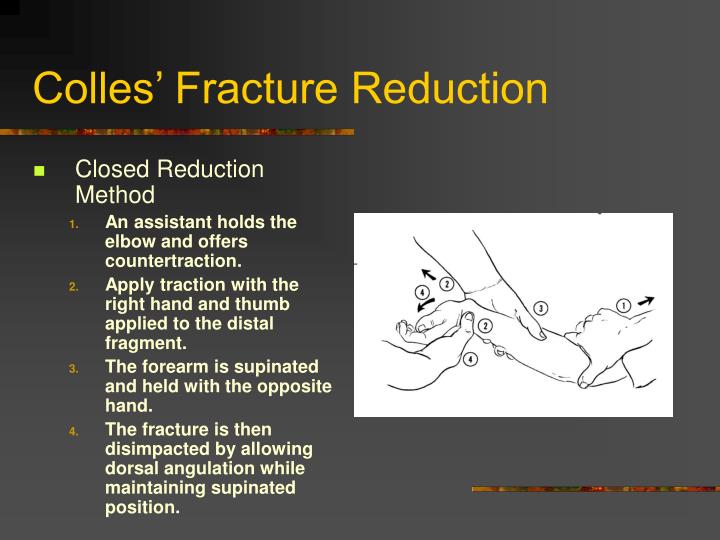
It is described this way because when fractured, the distal part of the radius moves upward creating an angle in the forearm near the wrist. The deformity which results from the Colles fracture is referred to as “having a dinner fork presentation”.
This fracture causes the radius to move upward to create an obvious and prominent deformity. It is more commonly found in older populations due to poor bone health, which leaves them more susceptible to breaks, but can also result from high impact collisions in sports which cause athletes to land on the hand and forearm. This kind of fracture results from an individual falling on to their outstretched hand. The most common operation used to treat fractures is called open reduction and internal fixation.A Colles fracture occurs on the distal part of the radius, the larger of two bones in the forearm. If the bone fragments are displaced and the fracture is unstable, surgery may be necessary. Timely follow-up will help your child's doctor discover this early and continue appropriate treatment. Occasionally, a week or two later, the bone may have lost its alignment and need to be corrected. A cast will protect the bones and hold them in proper position while they heal. Many growth plate fractures can heal successfully when treated with immobilization: A cast is applied to the injured area and the child limits some types of activity.ĭoctors most often use cast immobilization when the broken fragments of bone are not significantly out of place.
#Colles fracture rehab protocol crack
These fractures break through part of the bone at the growth plate and crack through the bone shaft, as well.
These fractures break through the bone at the growth plate, separating the bone end from the bone shaft and completely disrupting the growth plate. Perhaps the most widely used by doctors is the Salter-Harris system, described below. Several classification systems have been developed that categorize the different types of growth plate fractures. Other growth plate fractures, such as those around the knee, are associated with a higher rate of problems and therefore require very careful observation and follow-up. In some areas of the body, such as fingers in younger children, early diagnosis and treatment before healing has set in can sometimes prevent the need for more invasive treatments. How much the bone is out of alignment (displaced).Factors that affect the risk of problems over time include: Growth plate fractures vary greatly in terms of th risk for growth problems. They are also common in the outer bone of the forearm (radius) and lower bones of the leg (tibia and fibula). Most growth plate fractures occur in the long bones of the fingers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
